
During its peak, 120 Geminid meteors can be seen per hour under perfect conditions. Since that time, the Geminids have grown to become one of the most major showers of the year.
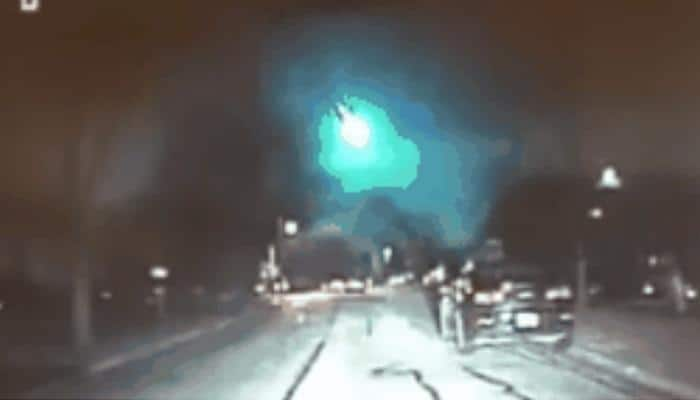

However, the first showers were not noteworthy with only 10 - 20 meteors seen per hour. The Geminids first began appearing in the mid-1800s. The Geminids, which peak during mid-December each year, are considered to be one of the best and most reliable annual meteor showers. Luckily the meteor shower will be going through the night.3200 Phaethon (an asteroid or a possible "rock comet")ħ9,000 mph (127,000 kph) or 22 miles per second (35 kilometers per second)


Be patient! You may not see anything right away.After about 30 minutes your eyes should be adjusted to the dark. Lie flat on your back with your feet facing the south and look up.Find an area well away from city or street lights.This shower is considered one of the best opportunities for young viewers since this shower starts around 9 or 10 p.m” Here are a few tips on how you can best observe the Geminids: How can you view the meteor shower? According to NASA: “The Geminids are best viewed during the night and predawn hours and are visible across the globe due to a nearly 24-hour broad maximum. Graphic on where to look to see the meteor shower (NASA). The Geminids first appeared in the mid 1800s. This asteroid gets its name from Phaëthon the son of the Greek god of the sun, Helos. They are in association with the 3200 Phaethon asteroid, which orbits the sun closer than any other asteroid. Each time a comet swings by the sun, it produces copious amounts of meteoroid sized particles which will eventually spread out along the entire orbit of the comet to form a meteoroid “stream.” If the Earth’s orbit and the comet’s orbit intersect at some point, then the Earth will pass through this stream for a few days at roughly the same time each year, encountering a meteor shower.” What is a meteor shower and what makes the Geminids different from other meteor showers? Per the AMS: “Most meteor showers have their origins with comets. Also, you should not look only to the constellation of Gemini to view the Geminids - they are visible throughout the night sky.” The constellation is not the source of the meteors. NASA denotes: “The constellation for which a meteor shower is named only serves to aid viewers in determining which shower they are viewing on a given night. The Geminid meteor shower gets its name as their apparent radiant (point in the sky they appear to come from) is in the constellation Gemini. During its peak, up to 120 meteors are visible per hour! The meteors are often bright and intensely colored. The Geminids are considered by the American Meteor Society (AMS), the most dependable and vibrant meteor showers of the year. The peak of the shower will be on the night of December 13 into the morning hours of the 14th. The Geminid meteor shower has been active! It began December 1, and is expected to end around December 22. Over 100 meteors are recorded in this composite image taken during the peak of the Geminid meteor shower in 2014.Ĭredit: NASA/MSFC/Danielle Moser, NASA’s Meteoroid Environment Office)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
